Setting The Default Page
Goals
Now that the structure is complete, let's make the flow work smoothly.
Currently when you go to your homepage you see the "Welcome aboard" message.
It would be easier to use our app if the homepage went directly to the topics list.
In this step we'll make that happen and learn a bit about routes in Rails.
Steps
Step 1: Add a root route
Open the file
config/routes.rbin an editor.Look for the line
Rails.application.routes.drawat the beginning of the file, and add the lineroot 'topics#index'after it. When you are done the start of the file should look like this:Rails.application.routes.draw do root 'topics#index'Step 2: Confirm your changes
Go back to your homepage. You should be taken to the topics list automatically.
Explanation
root 'topics#index'is a Rails route that says the default address for your site istopics#index.topics#indexis the topics list page (the topics controller with the index action).- Rails routes control how URLs (web addresses) get matched with code on the server. Similar to how addresses match with houses and apartments.
- The file
config/routes.rbis like an address directory listing the possible addresses and which code goes with each one
routes.rbuses some shortcuts so it doesn't always show all the possible URLs. To explore the URLs in more detail we can use the terminal.At the terminal type
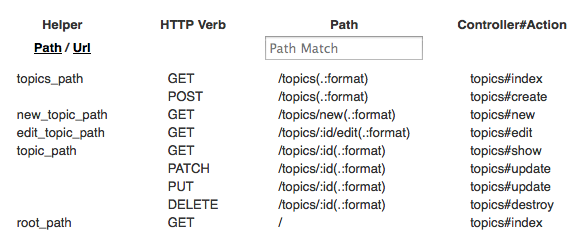
rails routes. You should get something that looks like this:$ rails routes Prefix Verb URI Pattern Controller#Action topics GET /topics(.:format) topics#index POST /topics(.:format) topics#create new_topic GET /topics/new(.:format) topics#new edit_topic GET /topics/:id/edit(.:format) topics#edit topic GET /topics/:id(.:format) topics#show PATCH /topics/:id(.:format) topics#update PUT /topics/:id(.:format) topics#update DELETE /topics/:id(.:format) topics#destroy root GET / topics#indexThis shows all the URLs your application responds to. The code that starts with colons are variables so :id means the id number of the record. The code in parenthesis is optional.
You can also get this information on your site in development. Go to /rails/info and you'll see something like this:
You'll also see that table in whenever you try to access an invalid route (try /sandwich)
Exploring Routes
Now you can have a look at the paths that are available in your app. Let's try looking at one of the topics routes we just generated. Open up your Rails console and play:
$ rails console >> app.topics_path => "/topics" >> app.topics_url => "http://www.example.com/topics"
appis a special object that represents your entire application. You can ask it about its routes (as we just did), play with its database connections, or make pseudo-web requests against it withgetorpost(and lots more).
Next Step:
Go on to Rails Architecture